Publications
Journal Articles
-
 Complex nonlinear dynamics of a multidirectional energy harvester with hybrid transductionL. G. Costa, and M. A. SaviOct 2024
Complex nonlinear dynamics of a multidirectional energy harvester with hybrid transductionL. G. Costa, and M. A. SaviOct 2024Mechanical energy harvesting has increasing scientific and technological interests due to novel energetic challenges. A critical issue in classical cantilever-based mechanical energy harvesting systems is the lack of multidirectional energy conversion capabilities and, due to that, deviations from the excitation source can drastically reduce their performance. This limitation has led to the development of energy harvesters with attached pendula, serving as a direction coupling mechanism. Nevertheless, the pendulum structure itself can act as an energy absorber, drastically reducing the harvester performance in certain scenarios. In order to overcome this issue, a hybrid multidirectional pendulum-based energy harvester has been introduced by the authors. The hybrid transduction integrates a piezoelectric element to capture energy from the principal direction and an electromagnetic transducer to harness rotational energy from the pendulum. This paper presents an in-depth analysis of the hybrid multidirectional pendulum-based energy harvester using a nonlinear dynamics perspective to evaluate the energy harvesting performance. A reduced-order model is proposed to represent the essential characteristics of such systems. A parametric analysis using a nonlinear dynamics perspective is carried out to map the system dynamics and performance. The emergence of complex and rich dynamics is observed, including chaos and hyperchaos. Results reveal the most and least effective combinations of structural parameters in terms of energy conversion. Additionally, the dynamical responses and patterns associated with high performance are identified. These responses are often characterized by a blend of irregular complex behaviors, coupled with a mix of oscillatory and rotational patterns of motion, resulting in wider bandwidth systems.
@article{Costa_multidirectional_EH_2, author = {Costa, L. G. and Savi, M. A.}, title = {Complex nonlinear dynamics of a multidirectional energy harvester with hybrid transduction}, journal = {Smart Materials and Structures}, volume = {33}, number = {11}, pages = {115007}, year = {2024}, month = oct, issn = {1361-665X}, doi = {10.1088/1361-665X/ad7ca7}, url = {https://dx.doi.org/10.1088/1361-665X/ad7ca7}, publisher = {IOP Publishing}, dimensions = {true}, xxgoogle_scholar_id = {WF5omc3nYNoC}, type = {journal} } -
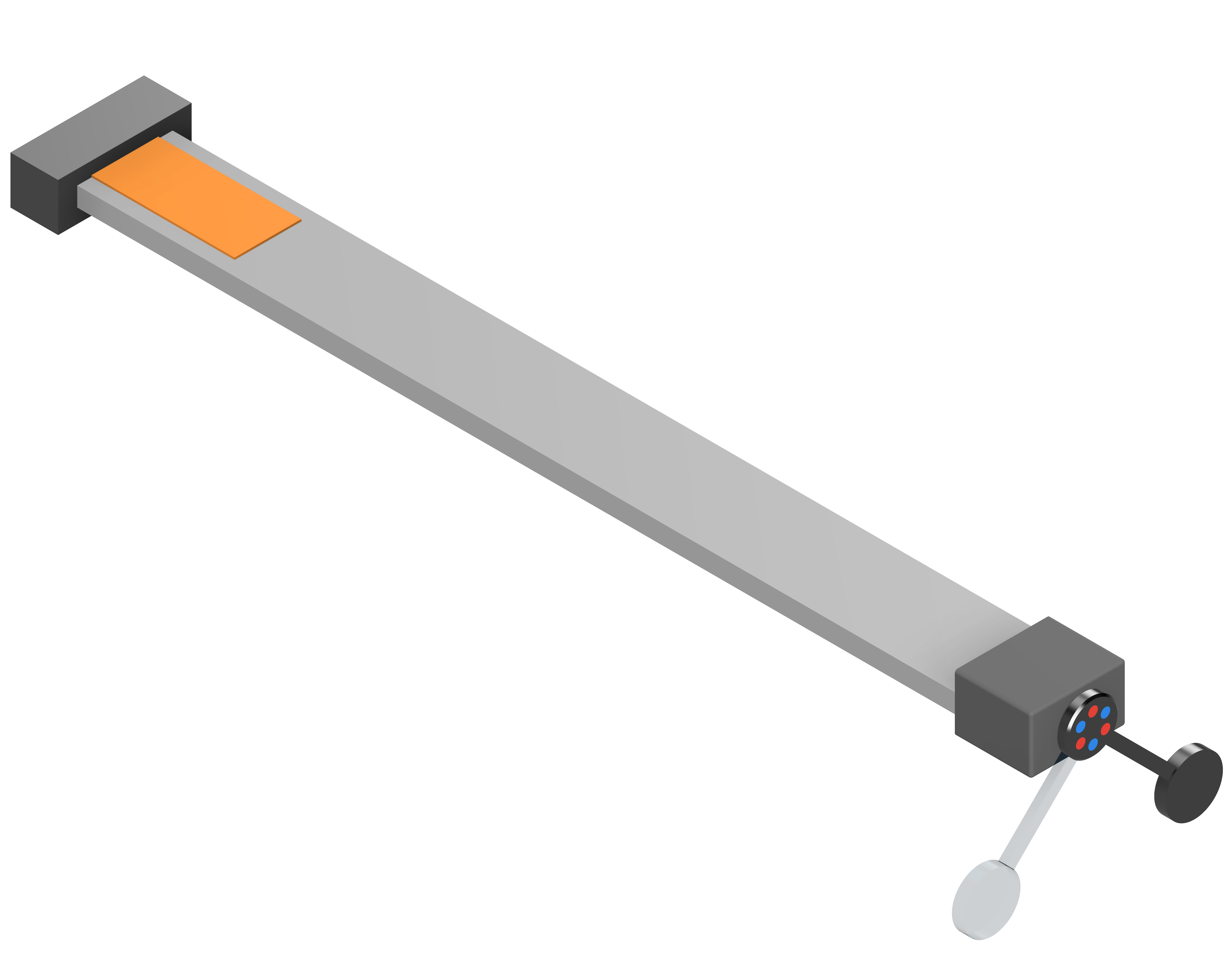 Pendulum-based hybrid system for multidirectional energy harvestingL. G. Costa, and M. A. SaviJul 2024
Pendulum-based hybrid system for multidirectional energy harvestingL. G. Costa, and M. A. SaviJul 2024This work presents a hybrid multidirectional mechanical energy harvester to enhance the performance of a cantilever-based harvester when subjected to multidirectional excitations. The multidirectional capabilities are achieved by employing a pendulum structure. Hybrid transduction is provided by combining a piezoelectric element and an electromagnetic transducer. A reduced-order model is presented based on the electromechanical Lagrangian formulation, and numerical analyses are performed to characterize the system behavior. A comparison based on energy harvesting performance is established among the novel multidirectional hybrid energy harvester (MHEH), the classical piezoelectric harvester (CPEH), and a multidirectional piezoelectric harvester (MPEH). Results show that the addition of the pendulum alone indeed provides multidirectional capabilities, but the overall performance can be reduced in some scenarios since it works as an energy absorber. This limitation is overcome by the hybridization strategy of the MHEH, by incorporating an electromagnetic transducer into the pendulum support. Overall, a significant improvement is achieved in all scenarios by utilizing the hybrid system.
@article{Costa_multidirectional_EH_1, author = {Costa, L. G. and Savi, M. A.}, title = {Pendulum-based hybrid system for multidirectional energy harvesting}, journal = {Nonlinear Dynamics}, volume = {112}, number = {21}, pages = {18665-18684}, year = {2024}, month = jul, issn = {1573-269X}, doi = {10.1007/s11071-024-10040-z}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-024-10040-z}, publisher = {Springer Nature}, dimensions = {true}, xxgoogle_scholar_id = {eQOLeE2rZwMC}, type = {journal} } -
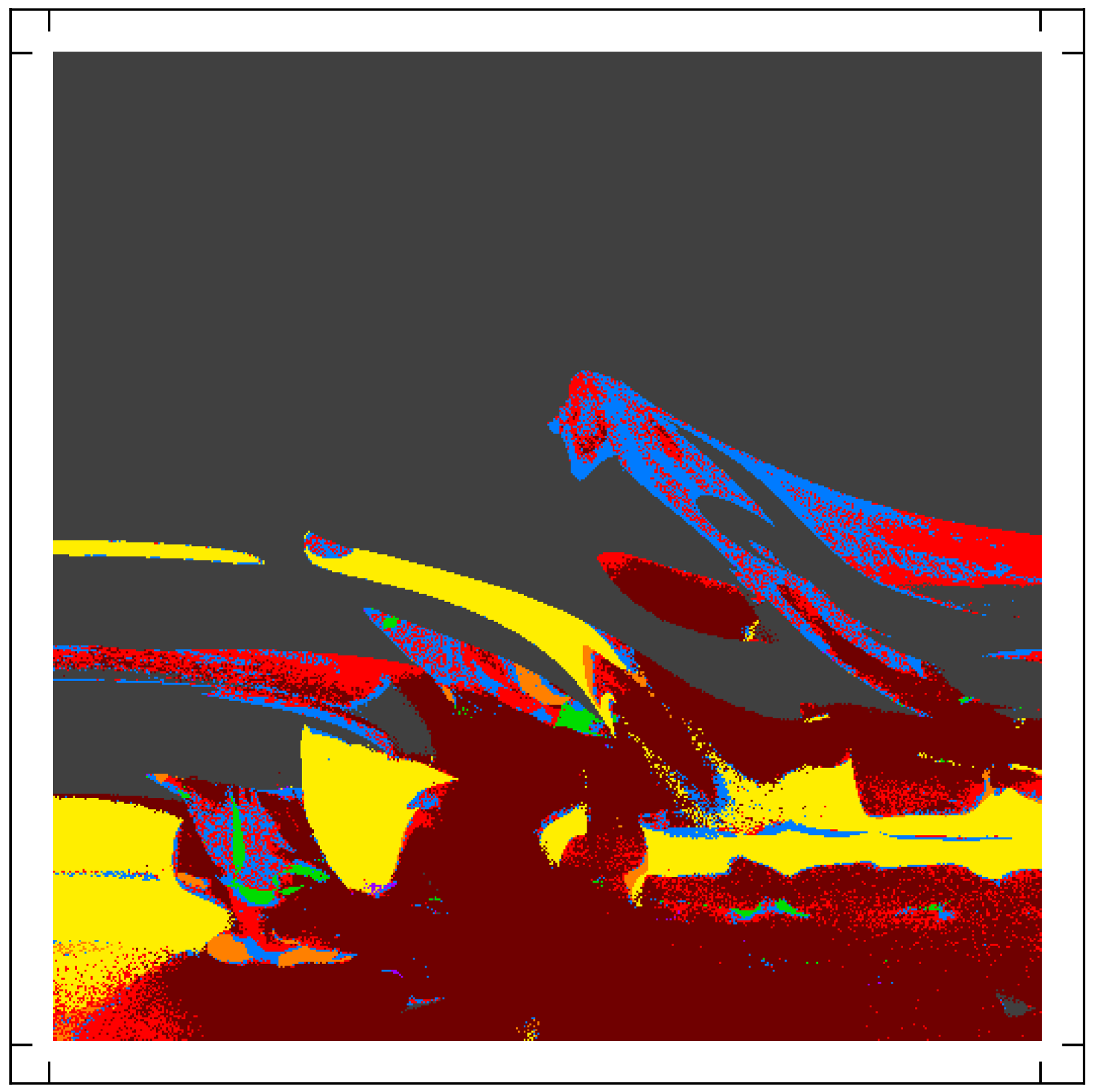
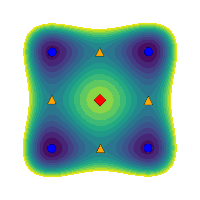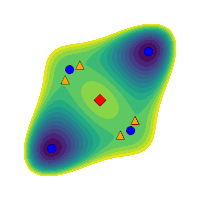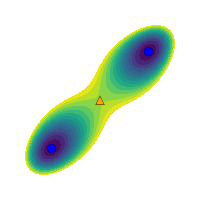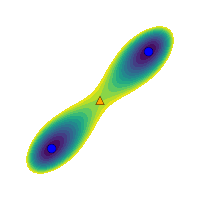 Multistability investigation for improved performance in a compact nonlinear energy harvesterL. G. Costa, L. L. S. Monteiro, and M. A. SaviMar 2024
Multistability investigation for improved performance in a compact nonlinear energy harvesterL. G. Costa, L. L. S. Monteiro, and M. A. SaviMar 2024Nature provides abundant ambient mechanical energy in the form of vibration, sound, wave, wind, and biomechanical energy, which can be harvested to power electronic systems. Smart materials-based mechanical energy harvesting systems have attracted increasing attention over the past two decades due to their advantageous characteristics such as high power density, simple design, and scalability. Nevertheless, the design of compact and high-performing systems remains a challenge. This work deals with the analysis of a compact multistable dual-beam nonlinear energy harvester that can be configured for different stability layouts. By using a nonlinear dynamics analysis framework and suitable tools, a qualitative performance characterization of the harvester for each stability configuration is conducted. Results show that multistable characteristics associated with a softer inner beam characteristic and higher excitation levels are related to complex phenomena and can greatly enhance performance.
@article{Costa_compact_EH_2, author = {Costa, L. G. and Monteiro, L. L. S. and Savi, M. A.}, title = {Multistability investigation for improved performance in a compact nonlinear energy harvester}, journal = {Journal of the Brazilian Society of Mechanical Sciences and Engineering}, volume = {46}, number = {4}, pages = {212}, year = {2024}, month = mar, issn = {1806-3691}, doi = {10.1007/s40430-024-04766-5}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-024-04766-5}, publisher = {Springer Nature}, dimensions = {true}, xxgoogle_scholar_id = {Tyk-4Ss8FVUC}, type = {journal} } -
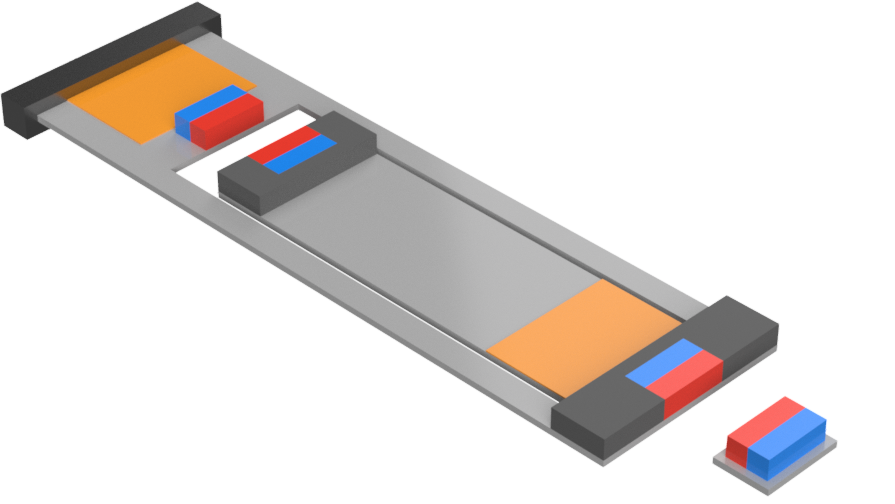 Nonlinear dynamics of a compact and multistable mechanical energy harvesterL. G. Costa, and M. A. SaviJan 2024
Nonlinear dynamics of a compact and multistable mechanical energy harvesterL. G. Costa, and M. A. SaviJan 2024The use of smart materials as transducers in mechanical energy harvesting systems has gained significant attention in recent years. Despite the numerous proposed solutions in the literature, challenges still exist in terms of their implementation within limited spaces while maintaining optimal performance. This paper addresses these challenges through the concepts of compactness and space-efficient design, as well as the incorporation of nonlinear characteristics and additional degrees-of-freedom. A multistable dual beam nonlinear structure featuring two magnetic interactions and two piezoelectric transducers is presented. A reduced order model with 2-degrees-of-freedom is established based on the harvester structure in order to capture the essential qualitative characteristics of the system. Stability analysis demonstrates that the combination of two nonlinear magnetic interactions furnish unprecedented multistable characteristics to this type of harvester. A framework using a nonlinear dynamics perspective is established to analyze multistable systems based on energy harvesting purposes. Different dynamical and stability characteristics are determined by the differences in the system stiffness ratio. Parametric analyses are carried out classifying regions of high performance in the external excitation parameter space. These regions are associated with rich and complex dynamics. Finally, a comprehensive comparison is conducted between the proposed harvester and the classical bistable harvester, revealing improvements in performance across nearly all relevant conditions. These findings highlight the enhanced capabilities of the proposed harvester design, solidifying its potential of application in diverse energy harvesting scenarios.
@article{Costa_compact_EH_1, author = {Costa, L. G. and Savi, M. A.}, title = {Nonlinear dynamics of a compact and multistable mechanical energy harvester}, journal = {International Journal of Mechanical Sciences}, volume = {262}, number = {}, pages = {108731}, year = {2024}, month = jan, issn = {0020-7403}, doi = {10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2023.108731}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2023.108731}, publisher = {Elsevier}, dimensions = {true}, xxgoogle_scholar_id = {zYLM7Y9cAGgC}, type = {journal} } -
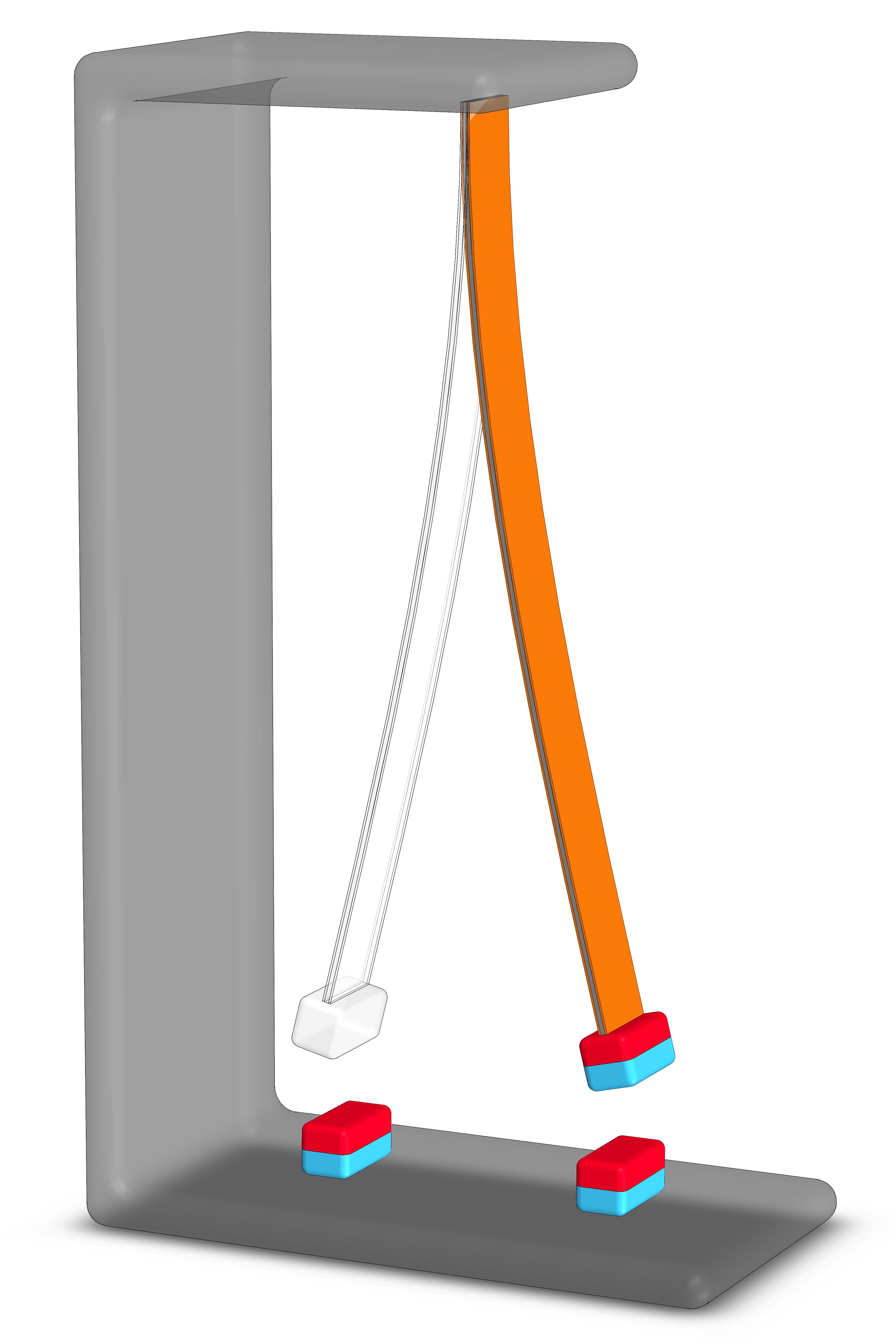 A parametric analysis of the nonlinear dynamics of bistable vibration-based piezoelectric energy harvestersApr 2021
A parametric analysis of the nonlinear dynamics of bistable vibration-based piezoelectric energy harvestersApr 2021Piezoelectric materials exhibit electromechanical coupling properties and have been gained importance over the last few decades due to their broad range of applications. Vibration-based energy harvesting systems have been proposed using the direct piezoelectric effect by converting mechanical into electrical energy. Although the great relevance of these systems, performance enhancement strategies are essential to improve the applicability of these system and have been studied substantially. This work addresses a numerical investigation of the influence of cubic polynomial nonlinearities in energy harvesting systems considering a bistable structure subjected to harmonic excitation. A deep parametric analysis is carried out employing nonlinear dynamics tools. Results show complex dynamical behaviors associated with the trigger of inter-well motion. Electrical power output and efficiency are monitored in order to evaluate the configurations associated with best system performances.
@article{Costa_bistable_EH, author = {Costa, L. G. and Monteiro, L. L. S. and Pacheco, P. M. C. L. and Savi, M. A.}, title = {A parametric analysis of the nonlinear dynamics of bistable vibration-based piezoelectric energy harvesters}, journal = {Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures}, volume = {32}, number = {7}, pages = {699-723}, year = {2021}, month = apr, issn = {1045-389X}, doi = {10.1177/1045389X20963188}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1177/1045389X20963188}, publisher = {Sage Journals}, dimensions = {true}, xxgoogle_scholar_id = {qjMakFHDy7sC}, type = {journal} }
Conference Articles
- DINAMENonlinear dynamics perspective framework employed to the analysis of energy harvestersL. G. Costa, and M. A. SaviApr 2025
Since the 1990s, mechanical energy harvesting smart structures have been developed to power low-power electronic devices. The wide variety of proposed designs has made their characterization and comparison increasingly challenging. This work presents and emphasizes the authors’ recent contributions to analyzing energy harvesting devices using a nonlinear dynamics perspective framework (NDPF). For that, four structures are examined, including two recently proposed designs by the authors and two classical devices established in the literature. The NDPF tools effectively map the dynamic and performance characteristics of these harvesters, allowing for a comprehensive comparison between its counterparts. Results demonstrate that NDPF analysis provides a robust solution for proper and accurate characterization of energy harvesting devices.
@inproceedings{DINAME_2025, author = {Costa, L. G. and Savi, M. A.}, title = {Nonlinear dynamics perspective framework employed to the analysis of energy harvesters}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the XX International Symposium on Dynamic Problems of Mechanics}, year = {2025}, publisher = {Associação Brasileira de Engenharia e Ciências Mecânicas (ABCM)}, address = {Águas de Lindóia, SP, Brazil}, doi = {10.26678/ABCM.DINAME2025.DIN2025-0124}, url = {https://doi.org/10.26678/ABCM.DINAME2025.DIN2025-0124}, dimensions = {false}, type = {conference} } - MECSOLMechanical energy multi-harvesting: on the performance enhancement of mechanical energy harvestersL. G. Costa, and M. A. SaviOct 2024
This work was recognized as the best student paper at the 9th International Symposium on Solid Mechanics.
Mechanical energy is manifested in the environment in various forms such as vibration, wind, sea waves, biomechanical motion, and sound. In this regard, the usage of different transducer mechanisms, especially smart materials, combined with mechanical nonlinear phenomena, has been extensively employed to convert mechanical into electrical energy, harnessing this kind of energy. Although many solutions are proposed, several challenges still exist in terms of implementation and performance. In this work, two recently proposed solutions for these challenges are summarized: the compactness of energy harvester to be implemented in confined spaces; and the ability to capture energy from multidirectional sources. These two solutions are distinguished by their multimodal characteristics associated with multi-transduction mechanisms. Results indicate that these features significantly enhance their energy harvesting capabilities, including maximum output power and bandwidth, outperforming classical counterparts.
@inproceedings{MECSOL_2024, author = {Costa, L. G. and Savi, M. A.}, title = {Mechanical energy multi-harvesting: on the performance enhancement of mechanical energy harvesters}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the 9th International Symposium on Solid Mechanics}, year = {2024}, month = oct, publisher = {Associação Brasileira de Engenharia e Ciências Mecânicas (ABCM)}, address = {Florianópolis, SC, Brazil}, doi = {10.26678/ABCM.MECSOL2024.MSL24-0088}, url = {https://doi.org/10.26678/ABCM.MECSOL2024.MSL24-0088}, dimensions = {false}, type = {conference}, } - CONEMAnalysis of a multidirectional hybrid energy harvesterL. G. Costa, and M. A. SaviJul 2024
Energy harvesting systems play an essential role in contemporary society, and ongoing research in the literature focuses on the development of more efficient designs that allow broader applications. In this regard, one promising approach is the use of hybrid systems that combine multiple transduction mechanisms, such as smart materials, electromagnetic coupling, and triboelectric effect. Another strategy consists of the addition of nonlinear characteristics, which often increase their performance. The source of multidirectionality is another important aspect that still remains a challenging topic. Therefore, the concept and performance of a nonlinear energy harvester that deals with hybrid transduction and multidirectionality is a challenging topic that needs to be investigated. This investigation addresses these challenges by incorporating a pendulum structure in a conventional cantilever-based piezoelectric energy harvester to enable multidirectional capabilities. A generic prototype model is presented to study the main characteristics of this type of system. The performance of the device is addressed and compared to its classical linear cantilever-based counterpart. Results show a significant performance improvement in all scenarios by utilizing the hybrid system.
@inproceedings{CONEM_2024, author = {Costa, L. G. and Savi, M. A.}, title = {Analysis of a multidirectional hybrid energy harvester}, booktitle = {Anais do XII Congresso Nacional de Engenharia Mecânica 2024}, year = {2024}, month = jul, publisher = {Associação Brasileira de Engenharia e Ciências Mecânicas (ABCM)}, address = {Natal, RN, Brazil}, doi = {10.26678/ABCM.CONEM2024.CON24-0218}, url = {https://doi.org/10.26678/ABCM.CONEM2024.CON24-0218}, dimensions = {false}, type = {conference} } - COBEMA prototype for multidirectional energy harvesting using pendulum structures and hybrid transductionL. G. Costa, and M. A. SaviDec 2023
The search for sustainable and renewable forms of energy supply has led to the development of new and creative ways to convert available environmental energy into useful electrical energy. In this regard, mechanical energy sources such as vibrations, wind, and ocean waves, are abundant and can be harnessed to power from small electronic devices to small urban centers. Electromagnetic converters, piezoelectric materials, triboelectric structures, and magnetostrictive materials can be cited as viable options for energy harvesting, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Energy harvesting systems that combines multiple transducer mechanisms have emerged as a promising trend in recent literature, as it has the potential to enhance energy harvesting capacity. Additionally, to ensure maximum efficiency in real-world applications, it is important to be able to harvest energy from multiple directions. This feature can be achieved by means of pendulum structures that can diffuse energy between directions within the system. This study investigates the combination of hybrid transducers and multidirectionality by analyzing a prototype of a hybrid electromagnetic-piezoelectric multidirectional energy harvester. Numerical analysis of the prototype are performed offering valuable insights about this type of electromechanical system. Results reveal that the addition of pendulum structures associated with hybrid transduction schemes can enhance energy harvesting performance significantly.
@inproceedings{COBEM_2023, author = {Costa, L. G. and Savi, M. A.}, title = {A prototype for multidirectional energy harvesting using pendulum structures and hybrid transduction}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the 27th International Congress of Mechanical Engineering}, year = {2023}, month = dec, publisher = {Associação Brasileira de Engenharia e Ciências Mecânicas (ABCM)}, address = {Florianópolis, SC, Brazil}, doi = {10.26678/ABCM.COBEM2023.COB2023-0655}, url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.26678/ABCM.COBEM2023.COB2023-0655}, dimensions = {false}, type = {conference} } - DINAMEAnalysis of mechanical energy harvesters using a nonlinear dynamics perspectiveL. G. Costa, and M. A. SaviFeb 2023
This communication was recognized as the best student work and presentation at the XIX International Symposium on Dynamic Problems of Mechanics.
Recent technological developments are demanding for self-powered electronic systems that need wireless and portable devices. In this regard, nonlinear mechanical energy harvesting systems are proving to be a reliable solution to turn wasted environmental mechanical energy into electrical energy by means of the direct piezoelectric effect. This work addresses a numerical characterization of two mechanical energy harvesting systems investigated based on nonlinear dynamics perspective. Results show complex dynamical patterns and highlight the best application scenario for each harvester.
@inproceedings{DINAME_2023, author = {Costa, L. G. and Savi, M. A.}, title = {Analysis of mechanical energy harvesters using a nonlinear dynamics perspective}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the XIX International Symposium on Dynamic Problems of Mechanics}, year = {2023}, month = feb, publisher = {Associação Brasileira de Engenharia e Ciências Mecânicas (ABCM)}, address = {Pirenópolis, GO, Brazil}, doi = {10.26678/ABCM.DINAME2023.DIN2023-0057}, url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.26678/ABCM.DINAME2023.DIN2023-0057}, dimensions = {false}, type = {conference}, } - CONEMNonlinear dynamics of an oscillator-pendulum energy harvesterL. G. Costa, V. J. Caetano, and M. A. SaviAug 2022
Recent developments and concepts in technology as cyber-physical systems, internet of things (IoT), cloud computing and wireless communication procedures require the use of self-powered sensors, actuators and small electronic devices. In this regard, mechanical energy harvesting systems are a promising and viable solution to power standalone devices by converting available environmental mechanical energy into electrical energy, especially through the direct piezoelectric effect. In the latest few decades, several systems have been proposed, many of them containing pendulum-like/bobbing structures in its composition. This work addresses a nonlinear dynamics investigation of a generic oscillator-pendulum energy harvester as a mean to achieve multidirectionality in the energy harvesting process. Numerical simulations are carried out employing the fourth order Runge-Kutta method. A parametric analysis is developed guided by nonlinear dynamics perspective, identifying the nuances and advantages of this kind of system. A performance analysis is carried out focusing on energy harvesting capacity. Results show complex dynamics and and increase in energy harvesting capacity for structures with a low ratio between natural frequencies in different directions.
@inproceedings{CONEM_2022, author = {Costa, L. G. and Caetano, V. J. and Savi, M. A.}, title = {Nonlinear dynamics of an oscillator-pendulum energy harvester}, booktitle = {Anais do XI Congresso Nacional de Engenharia Mecânica}, year = {2022}, month = aug, publisher = {Associação Brasileira de Engenharia e Ciências Mecânicas (ABCM)}, address = {Teresina, PI, Brazil}, doi = {10.26678/ABCM.CONEM2022.CON22-0434}, url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.26678/ABCM.CONEM2022.CON22-0434}, dimensions = {false}, type = {conference} } - MECSOLVibration energy harvesting using a two-degree of freedom Duffing-type structureL. G. Costa, L. L. S. Monteiro, and M. A. SaviOct 2022
The recent developments in technology and the emergence of Industry 4.0 have been motivating the study of optimized systems and new solutions to improve the employment of networks that use components as self-powered sensors, actuators and small electronic devices. In this regard, the scavenging of wasted forms of energy dissipated in the ambient is a topic that has been receiving great attention during the last few decades, especially the vibration energy. Composite structures utilizing piezoelectric materials are often employed to convert available mechanical energy into electrical energy exploiting the direct piezoelectric effect. In this work, a nonlinear two-degree of freedom Duffing-type energy harvesting system is proposed to enhance the performance of conventional devices. A discrete model is developed and numerical simulations are presented addressing the advantages and disadvantages of the system. Results show large operation bandwidths and power outputs, specially in higher frequencies.
@inproceedings{MECSOL_2022, author = {Costa, L. G. and Monteiro, L. L. S. and Savi, M. A.}, title = {Vibration energy harvesting using a two-degree of freedom Duffing-type structure}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Solid Mechanics}, year = {2022}, month = oct, publisher = {Associação Brasileira de Engenharia e Ciências Mecânicas (ABCM)}, address = {Campinas, SP, Brazil}, doi = {10.26678/ABCM.MECSOL2022.MSL22-0028}, url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.26678/ABCM.MECSOL2022.MSL22-0028}, dimensions = {false}, type = {conference} } - COBEMChaos and hyperchaos in a two-degree of freedom Duffing oscillatorL. G. Costa, L. L. S. Monteiro, and M. A. SaviNov 2021
The classical Duffing oscillator is often used to describe a great variety of physical phenomena. A deep nonlinear dynamics investigation of these systems is important to understand the nuances of the involved phenomena and their applications. This contribution deals with a parametric analysis of a two-degree of freedom Duffing oscillator. Stiffness coefficients are investigated for different stability configurations of the system. Besides, the external forcing parameters are also evaluated mapping and quantifying different types of responses. Numerical simulations are employed using fourth order Runge-Kutta method. Poincaré sections and Lyapunov exponents are employed to define different kinds of responses, characterizing periodic, chaotic and hyperchaotic behaviors. Results show a variety of complex behaviors associated with these types of systems.
@inproceedings{COBEM_2021_2, author = {Costa, L. G. and Monteiro, L. L. S. and Savi, M. A.}, title = {Chaos and hyperchaos in a two-degree of freedom Duffing oscillator}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the 26th International Congress of Mechanical Engineering}, year = {2021}, month = nov, publisher = {Associação Brasileira de Engenharia e Ciências Mecânicas (ABCM)}, address = {Florianópolis, SC, Brazil (Online)}, doi = {10.26678/ABCM.COBEM2021.COB2021-0402}, url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.26678/ABCM.COBEM2021.COB2021-0402}, dimensions = {false}, type = {conference} } - COBEMEnergy harvesting from chaotic vibrationL. G. Costa, E. V. M. Reis, and M. A. SaviNov 2021
Recent developments in technology requires the employment of self-powered sensors, actuators and small electronic devices. Energy harvesting systems are useful to this goal and can be configured in many different ways to improve process efficiency. The converted energy can also be stored to be further consumed. Mechanical vibration is one of the energy sources that can be converted into electrical energy. Besides the energy harvested, it is possible to mitigate undesirable vibrations. Smart materials are usually employed in these systems in order to promote electro-mechanical conversion. Piezoelectrics are smart materials employed to several applications in industry. Nonlinear characteristics are usually exploited in order to enhance energy harvesting capacity. In this regard, multistable energy potential is usually exploited by adding magnetic interactions to the system, being described by a Duffing-type system. Duffing oscillator has a rich dynamical behavior including chaos. In this regard, nonlinear dynamics analysis is essential for a proper design of the energy harvesting system. An important issue to be investigated is the correlation between energy harvesting capacity and the kind of response, which makes essential the use of proper nonlinear tools for a deep dynamical analysis. This paper addresses the correlation between the maximum Lyapunov exponent and power harvesting parameters in order to define harvesting capacity. Among the possibilities to be investigated, it should be highlighted the output RMS power and the efficiency of the energy conversion. This analysis allows one to connect the degree of chaoticity, represented by the value of Lyapunov exponents, with the electro-mechanical conversion efficiency.
@inproceedings{COBEM_2021_1, author = {Costa, L. G. and Reis, E. V. M. and Savi, M. A.}, title = {Energy harvesting from chaotic vibration}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the 26th International Congress of Mechanical Engineering}, year = {2021}, publisher = {Associação Brasileira de Engenharia e Ciências Mecânicas (ABCM)}, address = {Florianópolis, MG, Brazil (Online)}, doi = {10.26678/ABCM.COBEM2021.COB2021-0404}, url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.26678/ABCM.COBEM2021.COB2021-0404}, dimensions = {false}, type = {conference} } - COBEMNonlinear effects on experimental piezomagnetoelastic energy harvestingOct 2019
Recently, the study of the conversion of vibrational energy into electrical power has become an important field of research for clean and renewable energy resources. That concept has been improved on smart material field, due the last decade technological achievements on piezoelectric materials. Further, several low power devices as sensor and actuators were developed, so the energy harvesting through piezoelectric materials excited by environmental vibrations become a potential energy source on engineering. However, researchers still face challenges for the low energy efficiency of those conventional devices. The bistable energy harvesting devices have drawn significant attention due to some of their unique features, that method may enhance those devices efficiencies. This paper investigates a piezomagnetoelastic systems that consists of a permanent magnet fixed to the end of a piezoelectric cantilever which interacts with another magnet placed close to the free end of the cantilever, when the system is subjected to a harmonic base excitation. The magnets generate nonlinear repulsive force and make the structure bistable. The nonlinear energy harvester responds to vibration with large tip deflections and high energy orbit oscillations. Thus, the system can exhibit a broadened frequency response and sometimes chaotic motion, enhancing its energy harvesting potential.
@inproceedings{COBEM_2019_2, author = {Borges, G. X. G. and Costa, L. G. and Adeodato, A. and T., Duarte B. and Monteiro, L. L. S. and Pacheco, P. M. C. L. and Savi, M. A.}, title = {Nonlinear effects on experimental piezomagnetoelastic energy harvesting}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the 25th International Congress of Mechanical Engineering}, year = {2019}, month = oct, publisher = {Associação Brasileira de Engenharia e Ciências Mecânicas (ABCM)}, address = {Uberlândia, MG, Brazil}, doi = {10.26678/ABCM.COBEM2019.COB2019-0865}, url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.26678/ABCM.COBEM2019.COB2019-0865}, dimensions = {false}, type = {conference} } - COBEMA parametric analysis of the nonlinear dynamics of a duffing oscillatorL. G. Costa, L. L. S. Monteiro, and M. A. SaviOct 2019
This contribution deals with a parametric analysis of a Duffing oscillator. Nonlinear stiffness coefficients are investigated treating monostable and bistable systems. Besides, the external forcing is evaluated on system dynamics, mapping and quantifying different types of responses of the dynamical system. Numerical simulations are employed using fourth order Runge-Kutta method and Lyapunov exponents are used to define chaotic behavior. A statistical analysis is developed establishing the probability of each kind of response to occur. Results show a variety of complex behaviors associated with bistable systems.
@inproceedings{COBEM_2019_1, author = {Costa, L. G. and Monteiro, L. L. S. and Savi, M. A.}, title = {A parametric analysis of the nonlinear dynamics of a duffing oscillator}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the 25th International Congress of Mechanical Engineering}, year = {2019}, month = oct, publisher = {Associação Brasileira de Engenharia e Ciências Mecânicas (ABCM)}, address = {Uberlândia, MG, Brazil}, doi = {10.26678/ABCM.COBEM2019.COB2019-0258}, url = {http://dx.doi.org/10.26678/ABCM.COBEM2019.COB2019-0258}, dimensions = {false}, type = {conference} }
Theses
- Ph.D. ThesisAnalysis of Mechanical Energy Harvesters Using a Nonlinear Dynamics PerspectiveL. G. CostaFederal University of Rio de Janeiro, May 2024
Nature manifests mechanical energy in various forms including vibration, sound, waves, wind, and biomechanics, which can be harnessed to power electronic systems. Energy harvesting using smart materials allied with mechanical nonlinear phenomena has gained attention for its high power density, simple design, scalability, and improved performance. Despite many proposed solutions, implementation challenges remain. Nonlinear characteristics trigger complex dynamics, directly affecting performance. Thus, a proper analysis requires the harvester’s deep characterization guided by a nonlinear dynamics perspective. This work proposes a nonlinear dynamics framework of analysis for energy harvesting systems, addressing two recent challenges: harvesters in confined spaces, and energy harvesting from multidirectional sources, both while maintaining optimal performance. To deal with confined spaces, a novel compact structure is proposed with two pairs of magnetic interactions and piezoelectric transducers, revealing unprecedented multistable features. Analysis of different configurations successfully associates high-displacement period-3, period-1, and chaotic dynamics with higher performances. Comparisons with the classical bistable harvester highlight considerable performance enhancements. The multidirectional energy harvesting considers the use of pendulum structures, proposing a device that combines piezoelectric and electromagnetic transducers. Analysis of three configurations demonstrates that hybrid multitransduction is crucial for effective energy conversion. A parametric analysis maps the system dynamics and performance, revealing complex and irregular behaviors characterized by a combination of oscillation and rotational motion, leading to wider bandwidth systems.
@phdthesis{phd_thesis, author = {Costa, L. G.}, title = {Analysis of Mechanical Energy Harvesters Using a Nonlinear Dynamics Perspective}, school = {Federal University of Rio de Janeiro}, year = {2024}, address = {Rio de Janeiro, Brazil}, month = may, type = {thesis}, dimensions = {false}, }
